For tests drives of electric vehicles, high-frequency currents and voltages must be measured in the high-voltage vehicle electrical system. The installation options for the necessary measurement equipment can be very limited due to confined installation spaces. This example shows how currents and voltages can nevertheless be measured with high sampling rates, HV-safe and protected from environmental influences.
Background
Components in the electric powertrain as well as the complete HV electrical system of electrified vehicles are extensively tested in both simulations and on test benches. Nevertheless, current, voltage and power must also be measured in road tests to validate the development results under real conditions. This is the only way to obtain accurate results for the many necessary optimization steps.
For the measurement of current, voltage and power in the HV electrical system on test benches and in the vehicle, CSM’s HV Breakout Modules (https://s.csm.de/charged-bm) are a proven solution: They represent the most compact and least interference-sensitive measurement technology solution for such measurement tasks. The HV Breakout Modules have a robust housing for mobile use in vehicles and measure up to 2,000 A and 2,000 V with a high sampling rate of up to 2 MS/s. To meet EN61010:1 safety requirements, the HV power cables are connected directly inside the HV-safe housing
Due to the direct measurement from the inner conductors (also possible for current on the braided shields), extremely precise measurement results are achieved.
Challenge
The available installation space in the vehicle may be too small for traditional instrumentation due to tightly installed components and narrow cable ducts for installation. In such cases, another solution must be found for measuring current, voltage and power in road testing.
First and foremost, the measurement technology used must be able to be installed at the desired measurement points. Sometimes narrow cable ducts or surrounding components limit the available installation space. For this reason, the measurement technology used must then be designed to be even more compact, and be able to be used anywhere on the vehicle.
Nevertheless, very precise measurement results must be achieved, which is why the measurements need to be taken directly in the inner conductor otherwise the results will be falsified by induced shield currents and interference. In order to prevent missed (aliased) data, measurements need to be made at a sampling rate of at least 1 MHz.
The measurement technology must have robust housings in order to ensure high-voltage safety for users and systems, on the one hand and to be protected from harsh environmental conditions on the other.
The CSM Measurement Solution
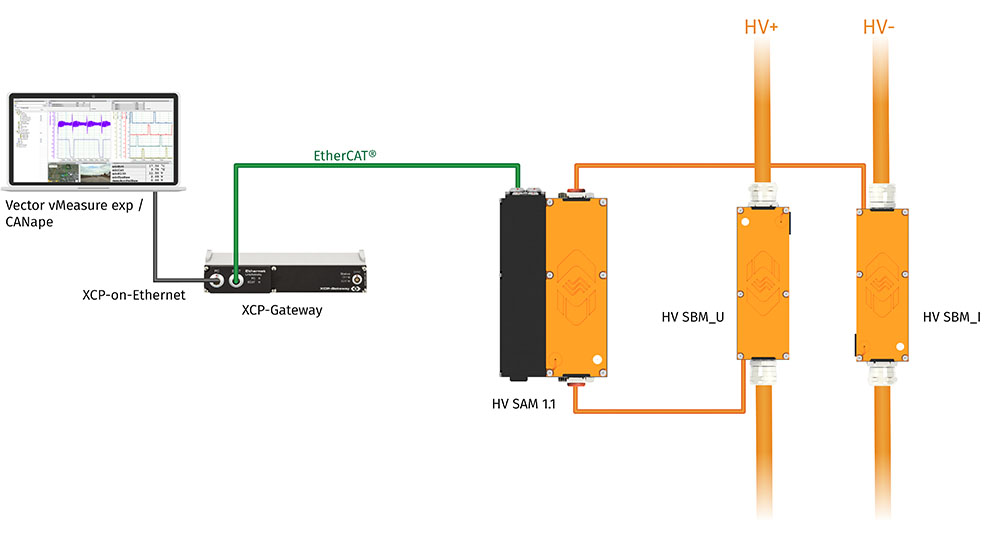
As an evolution of the previously mentioned HV BM product line, the new HV BM Split Modules (https://s.csm.de/charged-split) are used for measuring current, voltage and power in very confined installation spaces. High-voltage Breakout Modules of the Split family (HV BM Split Modules) use the same measuring principle as the CSM HV Breakout Modules for measurements in the vehicle electrical system. However, the three main functions are performed in their own small HV-safe enclosures, thus being “split” from each other. These 3 functions and split modules are
- HV SBM_I (HV Split Breakout Module for current): Current measurement with temperature compensated shunt module
- HV SBM_U (HV Split Breakout Module for voltage): direct measurement of Voltage
- HV SAM (HV Split Acquisition Module): Acquires the measurement data of the 2 SBM’s and puts that data onto the measurement network for further DAQ by a computer or logger.
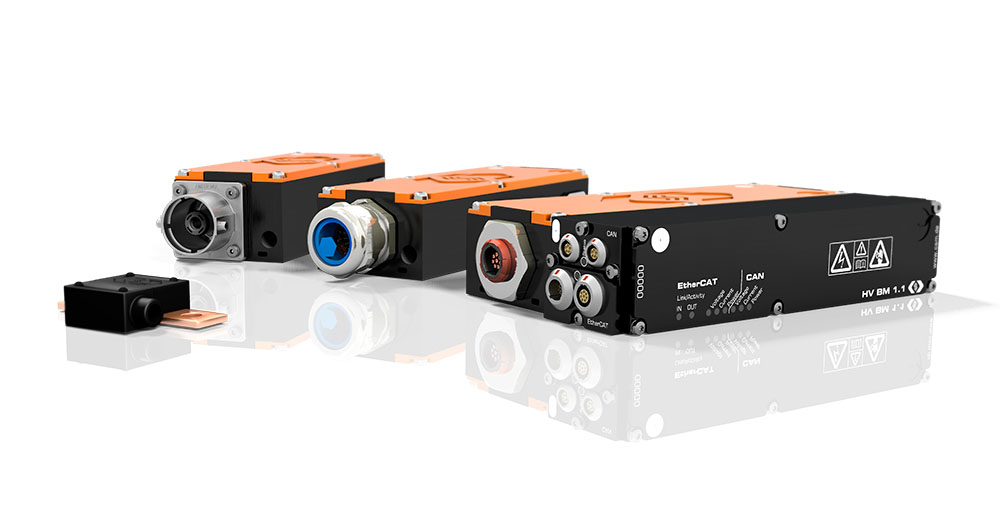

By separating the three main HV BM functions, the space required for installation in HV power cables or in busbars is greatly reduced. The HV SBMs are inserted directly into the HV cables via cable glands and ring terminals or PL300/PL500 connectors. The cable shield is routed separately, as with the HV Breakout Modules.
The current and voltage Split Breakout Modules are connected to the Split Acquisition Module via shielded high-voltage sensor cables with specialized connectors making the system safe. This allows the slim HV SBMs to be used individually in confined spaces and located up to 2m away from the HV SAM
The HV SAM performs sampling, AD conversion, filtering, online calculations, data acquisition, protocol conversion, and galvanic isolation. As with the standard HV Breakout Modules, data output is via EtherCAT® or CAN with up to 1 MHz data rate.
The measurement data output via EtherCAT® is converted to XCP-on-Ethernet via an XCP-Gateway and forwarded to the measuring computer. Further measurement modules for the acquisition of additional measured variables (such as temperature, pressures, vibration, noise, strain) can be easily integrated via the XCP-Gateway.
Benefits
The HV BM Split Modules enable precise current, voltage, and power measurements in very confined spaces. They use the proven technology of the HV Breakout Modules for accurate measurement results: Current measurement with shunt modules directly in the HV cables minimizes the influence of external fields, such as those that occur in magnetic field or Hall effect-based solutions. Pseudo-signals, hysteresis effects, system-related noise, characteristic shift or offset errors are practically non-existent with CSM shunt technology.
The sensor modules of the HV BM Split Modules are hardly larger than the HV lines themselves and can be installed in suitable locations. Measurements on closely installed high-voltage auxiliary consumers such as compressors, pumps, converters or braking resistors are thus made possible.
The HV BM Split modules are part of the Vector CSM E-Mobility Measurement System. They expand the decentralized, scalable measurement system for high-voltage current and voltage measurement in confined vehicle installation spaces for E-Mobility online analysis with CANape and vMeasure exp.
Download the full application example here: https://s.csm.de/charged-uc
Source: Electric Vehicles Magazine








 How refreshingly normal. This is good. Very good. That sums my first notes when driving the Mercedes-Benz EQB this past week, out from a Black Forest hotel with a mean umlaut, jetlagged, into the kind of muggy, scorching day—read 99 degrees—that puts one’s tolerance for hot air on high alert. Here, I wasn’t navigating…
How refreshingly normal. This is good. Very good. That sums my first notes when driving the Mercedes-Benz EQB this past week, out from a Black Forest hotel with a mean umlaut, jetlagged, into the kind of muggy, scorching day—read 99 degrees—that puts one’s tolerance for hot air on high alert. Here, I wasn’t navigating…


